TPRM lifecycle
The Third-Party Risk Management (TPRM) lifecycle is a comprehensive framework that guides organisations through the various stages of effectively managing risks associated with third-party relationships. This lifecycle encompasses a series of interconnected phases, each designed to ensure a proactive and systematic approach to identifying, assessing, mitigating, and monitoring third-party risks.
By adhering to a well-defined TPRM lifecycle, organisations can foster resilient partnerships, maintain compliance, and safeguard their operations from potential threats and vulnerabilities.
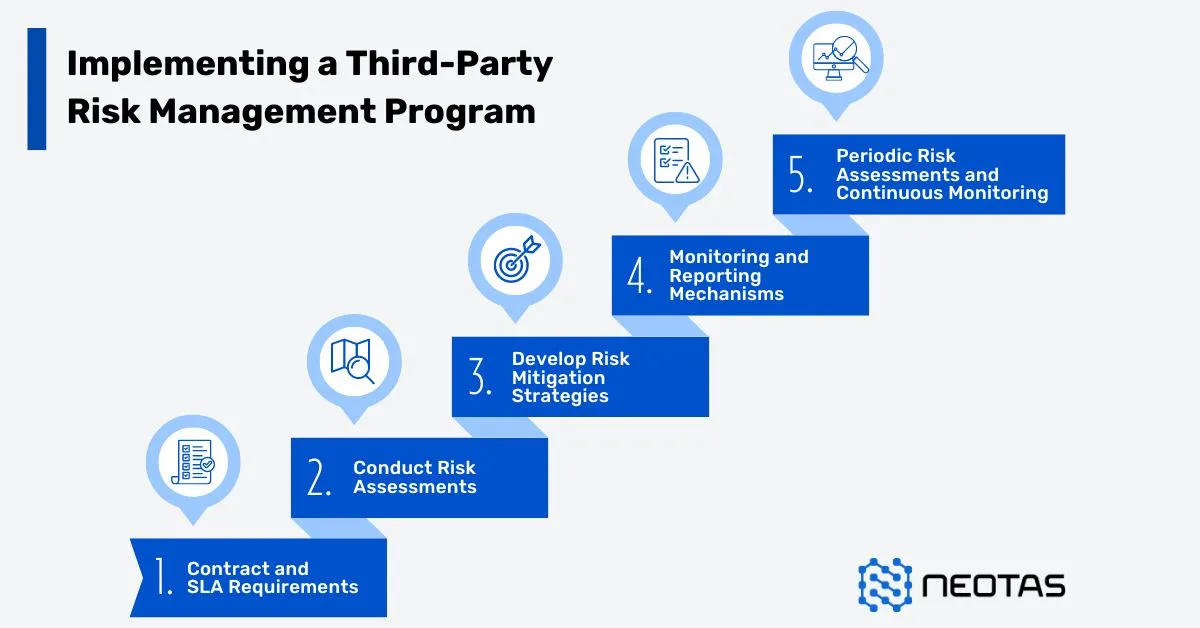
1. Establish Governance and Framework:
The TPRM lifecycle begins with the establishment of a robust governance structure and framework. This foundational phase involves defining clear roles, responsibilities, and accountability for managing third-party risks across the organisation. It entails developing comprehensive policies, standards, and procedures that align with the organisation’s overall risk management strategy and regulatory requirements.
Key activities in this phase include:
– Forming a cross-functional TPRM committee or working group
– Developing a TPRM policy outlining the organisation’s approach, objectives, and expectations
– Defining risk assessment methodologies and criteria
– Establishing risk reporting and escalation protocols
2. Third-Party Identification and Profiling:
The next phase involves identifying and profiling all third-party relationships within the organisation’s ecosystem. This comprehensive inventory should capture detailed information about each third party, including the nature of the services or products provided, the criticality of the relationship, the sensitivity of data shared, and the potential impact on the organisation’s operations.
Key activities in this phase include:
– Creating and maintaining a centralised third-party inventory
– Classifying third parties based on risk factors and criticality
– Gathering relevant documentation and information about third parties
– Conducting initial due diligence and background checks
3. Risk Assessment and Analysis:
Once third-party relationships have been identified and profiled, organisations must conduct thorough risk assessments to evaluate the potential risks associated with each relationship. This phase involves leveraging standardised risk assessment methodologies, such as questionnaires, on-site audits, or third-party risk assessment tools, to gather and analyse relevant information.
Key activities in this phase include:
– Assessing third-party cybersecurity posture, data protection practices, and operational resilience
– Evaluating compliance with relevant regulations and industry standards
– Identifying and analysing specific risks related to data breaches, operational disruptions, and regulatory non-compliance
– Calculating and assigning risk ratings based on likelihood and potential impact
4. Risk Mitigation and Treatment:
Based on the risk assessment findings, organisations must develop and implement tailored risk mitigation strategies to address identified risks. This phase involves prioritising risks based on their severity and criticality, and implementing appropriate controls and safeguards to reduce the organisation’s exposure.
Key activities in this phase include:
– Developing risk mitigation plans and strategies for high-risk third parties
– Implementing additional security controls, contractual terms, or training programs
– Negotiating and establishing comprehensive Service Level Agreements (SLAs)
– Terminating relationships with third parties posing unacceptable levels of risk
5. Contract Management and Ongoing Monitoring:
Effective contract management and continuous monitoring are crucial components of the TPRM lifecycle. This phase ensures that third-party relationships are governed by comprehensive agreements that clearly define expectations, responsibilities, and obligations. It also involves implementing mechanisms for regular monitoring and reporting of third-party performance, security incidents, and changes that may impact the risk profile.
Key activities in this phase include:
– Reviewing and negotiating third-party contracts and SLAs
– Establishing performance monitoring and reporting processes
– Conducting periodic risk reassessments and reviews
– Monitoring external sources for potential threats or vulnerabilities related to third parties
6. Incident Response and Remediation:
Despite rigorous risk management efforts, incidents and breaches may still occur. The TPRM lifecycle must address incident response and remediation processes to ensure prompt and effective handling of such events. This phase involves implementing robust incident response protocols, conducting root cause analyses, and implementing corrective actions to mitigate the impact and prevent future occurrences.
Key activities in this phase include:
– Establishing incident response plans and procedures
– Conducting investigations and root cause analyses
– Implementing remediation measures and corrective actions
– Collaborating with third parties to address and resolve incidents
7. Continuous Improvement and Program Maturity:
The TPRM lifecycle is an iterative process that requires continuous improvement and ongoing efforts to enhance program maturity. This phase involves regularly reviewing and refining the TPRM program’s processes, policies, and controls to ensure alignment with evolving business needs, regulatory changes, and industry best practices.
Key activities in this phase include:
– Conducting periodic program assessments and audits
– Incorporating lessons learned and feedback from stakeholders
– Benchmarking against industry standards and best practices
– Implementing process improvements and optimisations
– Fostering a culture of continuous learning and adaptation
8. Training and Awareness:
Effective TPRM requires a risk-aware culture that permeates the entire organisation and extends to third-party partners. This phase involves implementing comprehensive training and awareness programs to educate employees, third-party personnel, and stakeholders about the importance of TPRM, their roles and responsibilities, and best practices in managing third-party risks.
Key activities in this phase include:
– Developing training curricula and materials
– Conducting regular training sessions and awareness campaigns
– Promoting a culture of accountability and risk awareness
– Fostering collaboration and knowledge sharing among internal and external stakeholders
9. Reporting and Communication:
Transparent communication and reporting are essential for effective TPRM governance and stakeholder engagement. This phase involves establishing clear communication channels and regular reporting mechanisms to keep stakeholders informed about the TPRM program’s performance, identified risks, mitigation strategies, and overall risk posture.
Key activities in this phase include:
– Generating comprehensive risk reports and dashboards
– Communicating TPRM program updates and initiatives
– Facilitating cross-functional collaboration and information sharing
– Engaging with regulators and external auditors, as needed
10. Program Oversight and Governance:
Effective oversight and governance are paramount for ensuring the successful implementation and ongoing management of the TPRM program. This phase involves establishing a dedicated governance structure, such as a TPRM committee or working group, to oversee the program’s execution, monitor its performance, and ensure alignment with the organisation’s overall risk management strategy and regulatory requirements.
Key activities in this phase include:
– Establishing a TPRM steering committee or advisory board
– Conducting regular program reviews and assessments
– Ensuring adherence to policies, procedures, and regulatory requirements
– Providing strategic direction and decision-making support
– Fostering executive-level support and resource allocation
The TPRM lifecycle is a comprehensive and iterative process that requires a sustained commitment from the entire organisation. By diligently following this lifecycle, organisations can effectively identify, assess, mitigate, and monitor third-party risks, fostering resilient partnerships and maintaining a strong risk management posture. However, it is important to note that the TPRM lifecycle is not a one-size-fits-all approach; organisations must tailor and adapt it to their specific business needs, risk appetite, and regulatory environment, ensuring a customised and effective implementation.
Read more about Third-Party Risk, TPRM software, and TPRM processes.
Read the detailed guide on Vendor Due Diligence Checklist
TPRM lifecycle
How can Neotas TPRM solutions help?
Neotas offers an innovative solution to businesses grappling with Third-Party Risk Management (TPRM). In an era of increasing outsourcing, TPRM has become pivotal, and Neotas recognises this need. Through our enhanced due diligence platform, businesses can efficiently track and evaluate vendors and contractors, ensuring adherence to security protocols in a cost-effective manner.
The Neotas platform automates the vendor onboarding process, streamlining the addition of new vendors with remarkable ease and speed.
Moreover, Neotas provides a customisable dashboard, enabling businesses to proactively identify and address emerging risks. By consolidating vital vendor information, Neotas facilitates the seamless integration of risk management into existing Customer Relationship Management (CRM) and Supply Chain Management (SCM) systems, ultimately helping businesses maximise profits while minimising risk exposure.
If you’re curious about whether our third-party risk management solutions and services align with your organisation, don’t hesitate to schedule a call. We’re here to help you make informed decisions tailored to your needs.
Third Party Risk Management (TPRM) Solutions:
- Enhanced Due Diligence
- Management Due Diligence
- Customer Due Diligence
- Simplified Due Diligence
- Third Party Risk Management
- Vendor Due Diligence
- Open Source Intelligence (OSINT)
- Introducing the Neotas Enhanced Due Diligence Platform
Third Party Risk Management (TPRM) Case Studies:
- Third Party Risk Management (TPRM) Using OSINT
- Open-source Intelligence For Supply Chain – OSINT
- ESG Risk Management Framework with Neotas’ OSINT Integration
- Open Source Intelligence In AML Compliance | Case Study
- Identifying Difficult And Dangerous Senior Managers
- ESG Risk Investigation Uncovers Supply Chain Risks
- Financial Crime Compliance & Risk Management Trends
- Network Analysis Reveals International Links In Credit Risk Case
- Network Analysis and Due Diligence – Terrorist Financing
- Using OSINT For Sources Of Wealth Checks
- ESG Risks Uncovered In Investigation For Global Private …
- PEP Screening: Undisclosed Political Links Uncovered For European Organisation
- Risk-Based Approach (RBA) to AML & KYC risk management
- Anti-Money Laundering (AML)
- Supply Chain Risk Management
- Due Diligence Explained: Types, Checklist, Process, Reports



 Financial Crime Compliance Trends 2024
Financial Crime Compliance Trends 2024
























