AML Compliance Checklist
AML Compliance Requirements, AML Regulations and Best Practices for Anti-Money Laundering
Anti-Money Laundering (AML) compliance is essential for preventing illicit funds from infiltrating the legitimate financial system. Regulated entities, such as banks, financial institutions, and money service businesses, must implement effective AML programs to detect, prevent, and report money laundering activities. This comprehensive guide provides an in-depth look at AML compliance requirements, regulations, and best practices, ensuring that organisations can build robust AML programs that instill confidence in their operations.
What is AML Compliance?
AML Compliance refers to the adherence to laws and regulations designed to prevent money laundering. Money laundering involves concealing the origins of illegally obtained money, typically by passing it through a complex sequence of banking transfers or commercial transactions. AML compliance ensures that organisations have robust measures in place to detect and prevent these activities, thereby maintaining the integrity of the financial system.
Key Objectives of AML Compliance
- Prevent Illegal Activities: The primary goal of AML measures is to prevent money laundering and related financial crimes, including terrorist financing.
- Protect Financial Systems: AML practices safeguard the stability and integrity of financial systems from being exploited for criminal activities.
- Ensure Regulatory Compliance: Compliance with AML regulations helps institutions avoid legal penalties and reputational damage.
- Contribute to the Global Fight Against Financial Crimes: Effective AML measures support broader global efforts to combat financial crime.
AML Fundamentals
Definition and Scope
AML compliance encompasses a broad spectrum of measures and controls designed to detect, prevent, and report money laundering. These measures include:
- Customer Due Diligence (CDD): The process of identifying and verifying the identity of customers to assess their risk profiles.
- Transaction Monitoring: Ongoing scrutiny of transactions to identify unusual patterns that may indicate money laundering.
- Reporting Suspicious Activities: Procedures for reporting suspected money laundering activities to relevant authorities.
- Record Keeping: Maintaining comprehensive records of transactions and customer interactions to facilitate audits and investigations.
Key Objectives of AML Measures
- Prevent Illegal Activities: Detect and halt money laundering efforts before they can impact the financial system.
- Protect Financial Systems: Ensure that financial systems are not manipulated for illicit purposes.
- Ensure Regulatory Compliance: Meet legal and regulatory requirements to avoid fines and legal challenges.
- Enhance Transparency: Promote transparency and accountability within financial institutions.
AML Red-Flags
Identifying suspicious activities is a crucial part of AML compliance. Red flags are indicators that suggest potential money laundering or other financial crimes. These can include:
Unusual Transactions
Transactions that deviate from a customer’s normal behaviour or are unusually complex may indicate money laundering. Examples include:
- Large Cash Deposits: Significant cash deposits without a clear business rationale or source.
- Frequent Transfers: Rapid and frequent movements of funds between accounts without a logical purpose.
Common Red-Flags
- Sudden Increase in Account Activity: A sharp rise in transaction volume, particularly involving large sums, can be a sign of money laundering.
- Transactions Involving High-Risk Jurisdictions: Engaging in transactions with countries known for weak AML controls or high levels of corruption.
- Use of Multiple Accounts: Opening and using numerous accounts without a clear business or personal reason may indicate an attempt to obscure the origins of funds.
AML Screening
Customer Due Diligence (CDD)
Customer Due Diligence (CDD) is a fundamental component of AML compliance. It involves:
- Standard Due Diligence: Basic identification and verification of customers, including checking their identity and understanding their financial activities.
- Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD): More rigorous scrutiny for higher-risk customers, such as Politically Exposed Persons (PEPs) or individuals from high-risk jurisdictions. This involves additional checks and a more detailed assessment of the customer’s background and source of funds.
Sanctions Screening
Sanctions screening involves checking customers and transactions against relevant sanctions lists to ensure compliance with international sanctions regimes. This process helps identify individuals and entities that are prohibited from conducting business due to their involvement in criminal activities or associations with sanctioned regimes.
AML Monitoring
Ongoing Monitoring
Continuous monitoring of customer transactions and behaviours is essential for detecting and preventing suspicious activities. Automated systems are often employed to provide real-time monitoring and alert institutions to unusual patterns. Key aspects include:
- Automated Monitoring Systems: Technology that tracks and analyses transactions continuously to identify potential red flags.
- Manual Reviews: Complementing automated systems with manual reviews to ensure a comprehensive approach to monitoring.
Reporting Suspicious Activities
Clear procedures for reporting suspicious activities are vital. Institutions must have mechanisms in place to promptly inform relevant authorities about potential money laundering or other financial crimes. This includes:
- Suspicious Activity Reports (SARs): Detailed reports filed with financial intelligence units or regulatory bodies describing the nature of suspicious activities.
- Timely Reporting: Ensuring that reports are submitted in a timely manner to facilitate prompt investigation and action.
Risk Management
Risk-Based Approach
A risk-based approach to AML compliance involves tailoring measures to the specific risks faced by an institution. This approach ensures that resources are focused on higher-risk areas, enhancing the effectiveness of AML efforts. Key steps include:
- Identify Risks: Assess risks based on factors such as customer profiles, transaction types, and geographic locations.
- Mitigate Risks: Develop and implement strategies to address identified risks, such as enhanced monitoring for high-risk customers or transactions.
Risk Assessment and Mitigation
Regular risk assessments are essential for identifying and addressing emerging threats. This dynamic process involves:
- Periodic Reviews: Conducting regular reviews of AML policies and procedures to ensure they remain effective and relevant.
- Adapting to Changes: Adjusting AML measures in response to changes in the regulatory environment, emerging threats, or shifts in customer behaviour.
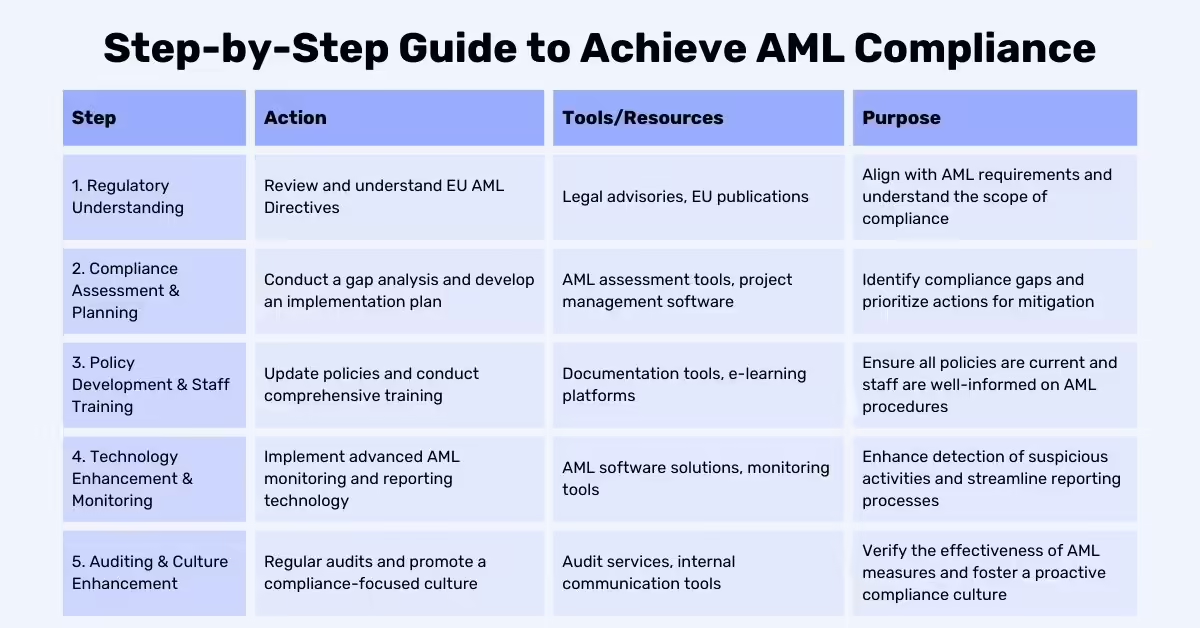
AML Regulations
Global and Regional Standards
AML regulations are guided by both global standards and regional specifics. Compliance with these regulations is essential for legal and ethical operation. Key regulatory bodies include:
- Financial Action Task Force (FATF): Provides global standards and recommendations for AML measures. FATF’s guidelines are widely adopted and influence AML regulations worldwide.
- European Union (EU) Regulations: Includes the EU Anti-Money Laundering Authority and the Single Rulebook, which aim to harmonise AML practices across member states and ensure consistent application of AML standards.
Compliance Requirements
Financial institutions must stay informed about changes in AML regulations to ensure ongoing compliance. This involves:
- Regular Updates: Monitoring and adapting to changes in global and regional AML regulations.
- Policy Reviews: Regularly reviewing and updating internal AML policies to align with current legal requirements.
AML Compliance Checklist
– A 10-Step Actionable Guide
Implementing an effective Anti-Money Laundering (AML) compliance programme is essential for financial institutions and other businesses at risk of being exploited for money laundering activities. This checklist outlines the key steps required to establish a robust AML compliance framework that meets regulatory requirements and protects your organisation from financial crime.
1. Establish an AML Compliance Officer
- Description: Appoint a qualified AML Compliance Officer responsible for overseeing the AML programme, ensuring compliance with relevant regulations, and acting as the primary contact with regulatory bodies.
- Actionable Steps:
- Choose a candidate with experience in AML regulations.
- Clearly define their roles and responsibilities.
- Ensure they have direct access to senior management.
2. Develop a Comprehensive AML Policy
- Description: Create an AML policy that outlines your organisation’s commitment to preventing money laundering and the procedures for identifying, assessing, and mitigating related risks.
- Actionable Steps:
- Draft a policy that covers all aspects of AML compliance, including customer due diligence, transaction monitoring, and reporting suspicious activities.
- Regularly review and update the policy to reflect changes in laws and regulations.
3. Implement Customer Due Diligence (CDD) Procedures
- Description: Conduct thorough due diligence on all customers to verify their identity, understand their financial activities, and assess their risk level.
- Actionable Steps:
- Collect and verify identification documents for all customers.
- Establish enhanced due diligence (EDD) procedures for high-risk customers.
- Maintain updated customer records and monitor for any changes.
4. Conduct Risk Assessments
- Description: Regularly assess the risks of money laundering within your organisation by evaluating customer profiles, geographic locations, products, services, and transactions.
- Actionable Steps:
- Use a risk-based approach to categorise customers and transactions.
- Continuously monitor for new or evolving risks.
- Document and update risk assessments periodically.
5. Implement Ongoing Transaction Monitoring
- Description: Monitor customer transactions in real-time to detect and report any unusual or suspicious activity that may indicate money laundering.
- Actionable Steps:
- Use automated systems to flag suspicious transactions based on predefined criteria.
- Regularly update transaction monitoring parameters to adapt to emerging threats.
- Investigate and document all flagged transactions.
6. Establish a Suspicious Activity Reporting (SAR) Process
- Description: Set up a process for promptly reporting suspicious activities to the relevant authorities, as required by law.
- Actionable Steps:
- Train employees on how to recognise and report suspicious activities.
- Establish a clear internal process for escalating and reviewing SARs before submission.
- Maintain records of all SARs filed, ensuring confidentiality.
7. Implement a Record-Keeping System
- Description: Maintain comprehensive records of all AML-related documents, including customer identification, transaction records, and SARs, for the required retention period.
- Actionable Steps:
- Ensure records are securely stored and easily retrievable.
- Implement data protection measures to safeguard sensitive information.
- Regularly audit record-keeping practices to ensure compliance with legal requirements.
8. Provide Regular AML Training to Employees
- Description: Educate all employees on AML laws, regulations, and internal procedures to ensure they understand their role in preventing money laundering.
- Actionable Steps:
- Develop an AML training programme tailored to the roles and responsibilities of different employees.
- Conduct training sessions regularly, including updates on new regulations and emerging threats.
- Track and document employee participation in AML training.
9. Perform Regular AML Audits
- Description: Conduct independent audits of your AML compliance programme to assess its effectiveness and identify areas for improvement.
- Actionable Steps:
- Schedule regular internal and external audits.
- Review audit findings with senior management and the AML Compliance Officer.
- Implement corrective actions for any identified deficiencies.
10. Review and Update the AML Programme Regularly
- Description: Continuously review and enhance your AML compliance programme to keep pace with regulatory changes, new threats, and evolving business practices.
- Actionable Steps:
- Set up a process for regularly reviewing and updating your AML policies, procedures, and systems.
- Engage with industry experts and regulators to stay informed about best practices.
- Ensure that all updates are communicated to employees and reflected in training materials.
This AML compliance checklist provides a structured approach to developing and maintaining an effective AML programme. By following these steps, your organisation can reduce the risk of being involved in money laundering activities, ensure compliance with regulatory requirements, and protect its reputation. Regular review and adaptation of your AML strategies are crucial to keeping your programme robust and effective in the face of evolving financial crime risks.
Download the detailed AML Checklist
Developing an Effective AML Compliance Programme
Creating a robust Anti-Money Laundering (AML) compliance programme is critical for financial institutions to protect against money laundering, terrorist financing, and other financial crimes. An effective AML compliance programme is built on several key components that work together to detect, prevent, and report suspicious activities.
1. Comprehensive Policies and Procedures
- Description: The foundation of a successful AML programme lies in well-documented policies and procedures. These should be tailored to the specific risks and operational structure of the institution.
- Key Elements:
- Risk-Based Policies: Develop policies that focus on the specific risks faced by the institution, including customer types, services offered, and geographical regions.
- Clear Procedures: Establish clear, step-by-step procedures for customer due diligence (CDD), ongoing monitoring, and the reporting of suspicious activities.
- Regular Updates: Periodically review and update policies to ensure they align with current regulations and emerging threats.
2. Strong Internal Controls
- Description: Implementing robust internal controls is essential to prevent and detect potential money laundering activities.
- Key Elements:
- Segregation of Duties: Ensure that critical functions, such as account opening and transaction approval, are handled by different employees to reduce the risk of fraud.
- Approval Processes: Set up multi-layered approval processes for high-risk activities to enhance oversight.
- Automated Monitoring Systems: Use technology to continuously monitor transactions for unusual patterns or behaviours that may indicate money laundering.
3. Effective Customer Due Diligence (CDD)
- Description: Conduct thorough due diligence to verify the identity of customers and assess their risk level.
- Key Elements:
- Identity Verification: Collect and verify information from reliable, independent sources to confirm the identity of customers.
- Risk Assessment: Categorise customers into risk levels (low, medium, high) based on factors such as the nature of their business, location, and transaction types.
- Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD): Apply additional scrutiny to high-risk customers, including obtaining more detailed information and monitoring their activities more closely.
4. Ongoing Employee Training
- Description: Regular training ensures that all employees are aware of AML regulations, their responsibilities, and how to recognise suspicious activities.
- Key Elements:
- Role-Specific Training: Provide training tailored to the roles and responsibilities of different staff members, from frontline employees to senior management.
- Updates and Refreshers: Offer regular refresher courses to keep staff informed of changes in AML regulations and emerging threats.
- Practical Scenarios: Use real-world case studies and scenarios to help employees apply their knowledge effectively.
5. Independent Audits and Testing
- Description: Regular independent audits and testing are vital to assess the effectiveness of the AML compliance programme and identify areas for improvement.
- Key Elements:
- Internal and External Audits: Conduct both internal and external audits to provide a comprehensive evaluation of the AML programme.
- Continuous Monitoring: Implement ongoing testing to ensure that controls are functioning as intended and that weaknesses are promptly addressed.
- Audit Follow-Up: Act on audit findings by implementing corrective measures and making necessary adjustments to policies and procedures.
6. Suspicious Activity Reporting (SAR)
- Description: Establish a clear process for identifying and reporting suspicious activities to the appropriate authorities in a timely manner.
- Key Elements:
- Timely Reporting: Ensure that suspicious activity reports (SARs) are filed as soon as suspicious behaviour is identified.
- Confidentiality: Maintain strict confidentiality regarding the details of SARs and the individuals involved.
- Documentation: Keep detailed records of all SARs filed, including the reasoning behind each report and any follow-up actions taken.
7. Regular Risk Assessments
- Description: Regularly assess the institution’s exposure to money laundering risks and adjust the AML programme accordingly.
- Key Elements:
- Dynamic Risk Assessment: Continuously evaluate the risk environment and adapt the AML programme to address new and evolving risks.
- Comprehensive Coverage: Assess risks across all aspects of the business, including customers, products, and geographical operations.
- Documentation and Review: Document the results of risk assessments and use them to inform updates to the AML policies and procedures.
Roles and Responsibilities in an AML Compliance Program
Effective AML compliance requires collaboration and accountability across the organisation. Key roles include:
- Compliance Officers: Responsible for developing and implementing AML policies, overseeing monitoring systems, and ensuring timely reporting of suspicious activities.
- Senior Management: Provides leadership, resources, and oversight, participates in risk assessments, and ensures overall accountability for AML compliance.
- Employees: Follow AML procedures, report suspicious activities, and engage in continuous learning to stay informed about AML requirements.
AML compliance is crucial for upholding the integrity and stability of the global financial system. By enforcing stringent AML measures, organisations not only prevent and combat money laundering but also protect their reputations and contribute to the worldwide effort against financial crime. Maintaining an effective AML compliance programme requires continuous improvement, adaptation to emerging threats, and strict adherence to regulatory requirements. Through the diligent application of these practices, financial institutions not only secure their operations but also play a vital role in fostering transparency and accountability across the global financial landscape.
A dynamic and robust AML compliance programme is an essential component of any financial institution’s risk management strategy. By implementing comprehensive policies, rigorous internal controls, ongoing training, and regular audits, institutions can more effectively mitigate the risks associated with money laundering and ensure compliance with ever-evolving regulations. Continuous adaptation to new threats is key to sustaining the effectiveness of the AML compliance programme over time.
About Neotas Due Diligence
Neotas Platform covers 600Bn+ archived web pages, 1.8Bn+ court records, 198M+ corporate records, global social media platforms, and 40,000+ Media sources from over 100 countries to help you build a comprehensive picture of the team. It’s a world-first, searching beyond Google. Neotas’ diligence uncovers illicit activities, reducing financial and reputational risk.
AML Solutions:
- Risk-Based Approach (RBA) to AML & KYC risk management
- Anti-Money Laundering (AML) Compliance
- Anti-Money Laundering (AML) Checks
- Anti-Money Laundering (AML) Regulations
- Anti-Money Laundering (AML) Compliance Checklist
- Anti-Money Laundering (AML) Compliance Checklist for Banks
- Anti-Money Laundering (AML) Transaction Monitoring
- Money Laundering Reporting Officer (MLRO) – Roles and Responsibilities of an MLRO
- What is Customer Due Diligence in Banking and Financial Services?
Due Diligence Solutions:
- Enhanced Due Diligence
- Management Due Diligence
- Customer Due Diligence
- Simplified Due Diligence
- Third Party Risk Management
- Open Source Intelligence (OSINT)
- Customer Due Diligence Requirements
- Introducing the Neotas Enhanced Due Diligence Platform
Due Diligence Case Studies:
- Case Study: OSINT for EDD & AML Compliance
- Overcoming EDD Challenges on High Risk Customers
- Neotas Open Source Intelligence (OSINT) based AML Solution sees beneath the surface
- ESG Risks Uncovered In Investigation For Global Private Equity Firm
- Management Due Diligence Reveals Abusive CEO
- Ongoing Monitoring Protects Credit Against Subsidiary Threat
- AML Compliance and Fraud Detection – How to Spot a Money Launderer and Prevent It
- What is Customer Due Diligence in Banking and Financial Services?
FAQs on AML Compliance
What is AML Compliance?
AML Compliance refers to the processes and regulations that financial institutions and businesses must follow to prevent money laundering and other financial crimes. It involves measures like customer due diligence, transaction monitoring, and reporting suspicious activities to ensure the financial system’s integrity.
Why is AML Compliance important?
AML Compliance is essential to prevent money laundering, protect financial systems from being exploited for illegal activities, ensure regulatory compliance, and contribute to global efforts to combat financial crime.
What are the key objectives of AML measures?
The key objectives of AML measures include preventing illegal activities, protecting the financial system, ensuring regulatory compliance, and enhancing transparency within financial institutions.
What is Customer Due Diligence (CDD) in AML?
Customer Due Diligence (CDD) involves verifying the identity of customers, understanding their financial activities, and assessing their risk level to prevent money laundering and other financial crimes.
What are the common AML red flags to watch for?
Common AML red flags include unusual transactions, large cash deposits without a clear rationale, frequent transfers between accounts, and transactions involving high-risk jurisdictions.
What is the role of a Suspicious Activity Report (SAR) in AML?
A Suspicious Activity Report (SAR) is a document filed by financial institutions to report suspected money laundering or other suspicious activities to relevant authorities. It is a crucial part of AML compliance.
How does ongoing transaction monitoring work in AML compliance?
Ongoing transaction monitoring involves continuously reviewing customer transactions to detect and report unusual or suspicious activities. Automated systems are often used to flag transactions based on predefined criteria.
What is a risk-based approach in AML compliance?
A risk-based approach in AML compliance involves tailoring AML measures to the specific risks faced by an institution, focusing resources on higher-risk areas to enhance the effectiveness of AML efforts.
What are the global standards for AML compliance?
Global standards for AML compliance are set by organisations like the Financial Action Task Force (FATF), which provides guidelines and recommendations that influence AML regulations worldwide.
What are the key components of an effective AML compliance programme?
Key components include comprehensive policies and procedures, strong internal controls, effective customer due diligence, ongoing employee training, independent audits and testing, suspicious activity reporting, and regular risk assessments.
What is Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD)?
Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD) is a more rigorous level of scrutiny applied to high-risk customers, such as Politically Exposed Persons (PEPs) or individuals from high-risk jurisdictions, involving additional checks and a detailed assessment of their background and source of funds.
How should organisations handle AML training for employees?
Organisations should develop AML training programmes tailored to the roles of different employees, conduct regular training sessions, provide updates on new regulations and emerging threats, and document employee participation.
What is the role of an AML Compliance Officer?
An AML Compliance Officer is responsible for overseeing the AML programme, ensuring compliance with relevant regulations, and acting as the primary contact with regulatory bodies. They play a critical role in the organisation’s AML efforts.
What should be included in an AML policy?
An AML policy should cover all aspects of AML compliance, including customer due diligence, transaction monitoring, reporting suspicious activities, and record-keeping. It should be regularly reviewed and updated to reflect changes in laws and regulations.
How often should AML compliance programmes be audited?
AML compliance programmes should be audited regularly, both internally and externally, to assess their effectiveness and identify areas for improvement. Regular audits help ensure that controls are functioning as intended and that any weaknesses are promptly addressed.



 Financial Crime Compliance Trends 2024
Financial Crime Compliance Trends 2024












